Dr. P. Srinivas, MD, DNB, DM Consultant – Cardiology (Adult)
What is a pacemaker?
A pacemaker is a device that sends small electrical impulses to the heart muscle to maintain a suitable heart rate and is used to treat patients with a condition known as bradyarrhythmias (slow heart rates or defective electrical conduction) that cause symptoms.
Brief history:
A 78-year-old gentleman presented to Narayana Multispeciality Hospital, Mysuru, with episodes of presyncope (near loss of consciousness) for 2 weeks. His ECG showed evidence of TachyBrady syndrome (a combination of abnormal fast and slow heart rates, both requiring treatment). Given his advanced age and possible Atrial fibrillation (documented later), he was advised a single chamber pacemaker (right ventricular) by a Senior Interventional Cardiologist Dr. P. Srinivas.
In consideration of his comorbidities, an innovative and ground-breaking technology called ‘Leadless pacemaker implantation’ was offered. The patient underwent successful leadless pacemaker implantation without any complication and was discharged in a couple of days.
What are the types of pacemakers available and what are the risks involved?
Conventional pacemakers require creating a surgical pocket in the upper part of the chest and entail procedural complications like lung injury, pocket collections by blood or infection and require connecting leads to a pulse generator placed under the skin. It can cause considerable pain, risks injury to nearby arteries or lung tissue and can have a negative cosmetic appeal for few; generally, a lump is seen and felt under the skin at the site of the pacemaker. The leads (thin cables connecting the pulse generator to heart muscle) are themselves subject to complications like insulation failure, compression, dislodgement and perforation. Patients are also required to limit their arm movements (on the side of the pacemaker) for the initial few weeks.
Who is a candidate for a leadless pacemaker?
Not everyone is a candidate for a leadless pacemaker. Currently, the device is available only for patients with symptomatic bradycardia who need a single chamber (the lower heart chamber) pacing only. Technology has advanced now to include mechanical sensing of the upper heart chamber as well, another major advantage being all current leadless pacemakers are MRI compatible.

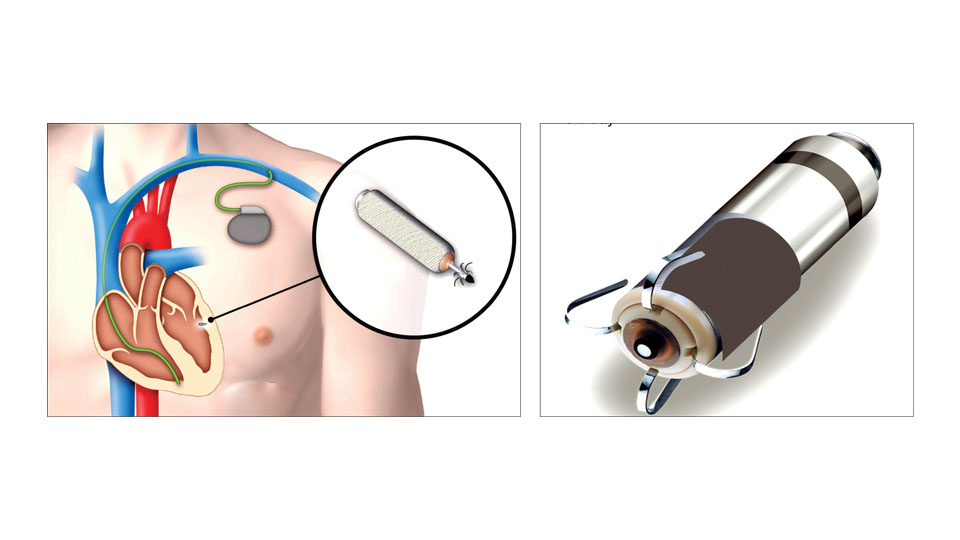
What is a leadless pacemaker and what are its advantages?
A leadless pacemaker is a small self-contained device that is inserted directly into the lower chamber of the heart. It is 90% smaller than a conventional pacemaker and contains all the components (generator and electrical system) of a regular pacemaker housed in a small capsule.
It is deployed by a simple procedure through the groin via a long tube called a catheter and does not require the creation of any pocket or incision in the chest nor any attachment to leads. It is indeed a medical marvel with a near painless experience for the patient eliminating nearly all the possible complications associated with a regular pacemaker and also having a cosmetic appeal. The patient can be mobilised the same day and may even be discharged home the very next day.
The Future: The future is exciting and promising as well, with new technology being developed in the field of pacing and might eventually lead to expanded pacing indications. It is a boon for patients requiring pacemaker therapy, provided the right clinical indication and appropriate patient selection protocols are followed.







Routine pacemaker procedure done in the hospitals in the West. The question here is the quality of this pacemaker, if made in India!