By Dr. Devdutt Pattanaik – Author, Speaker, Illustrator, Mythologist
It is common amongst Western scholars and their Westernised students to differentiate between the Vedic yagna and the Puranic puja, rituals that define the two major phases of Hinduism, one that flourished over 3,000 years ago and one that emerged 2,000 years ago. Of course, at the other extreme, we have the bhakta-Indologists who insist that Hinduism has no history, or phases, or evolution — that everything was homogenous and static, until Muslims came into the land 1,000 years ago. The truth is somewhere in between, as usual.
Vedic yagna is conventionally translated as ‘sacrifice’ and Puranic puja is translated as ‘worship’. This translation is the basic problem. Both are based on Christian templates of religion where God of Abraham demands sacrifice (giving up something dear for the pleasure of God) and worship (adoration, veneration of God). Anyone who has actually performed the two rituals, or at least studied the two rituals carefully, will notice that the sacrifice and worship constitutes only part of the ritual, the first half — the second half is about asking for something in return, the fruit of the sacrifice or ritual known as phala-stuti, which is common to both yagna and puja.
This makes yagna and puja essentially exchange with the divine. There is the giving part (sacrifice, and worship, if one wants to call it that); this is followed by the receiving part, or at least the desire for something in exchange. Anyone who performs a yagna or puja knows that the ritual always ends with asking for something, material or spiritual, from the divine. This exchange makes it different from a prayer.
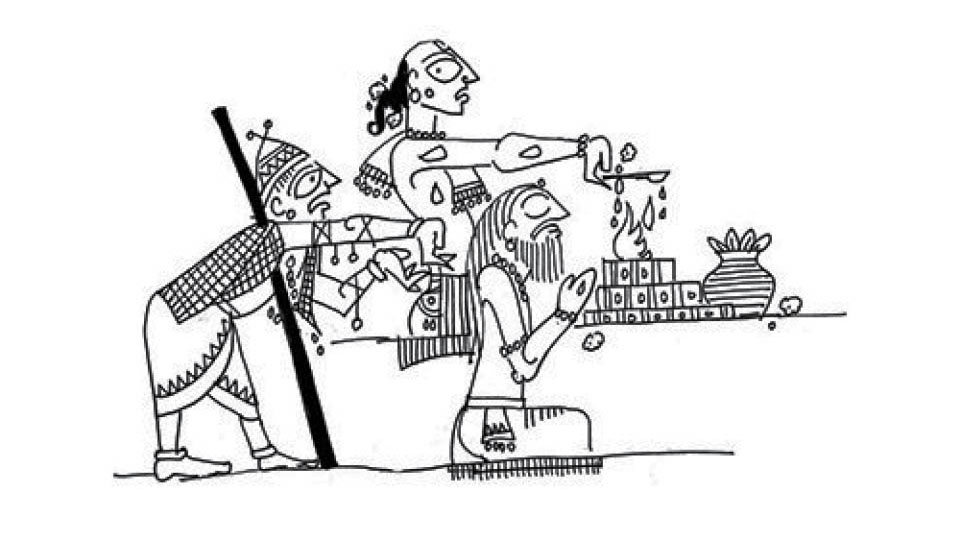
Yagna was designed by Brahmins 3,000 years ago as an elaborate ceremony to invite (avahan) celestial beings (deva) who rode celestial chariots (rathas). Communication was established using fire (agni) as medium, chants (mantra) and special offerings (soma). The yagna acknowledged through symbolic enactment and ritual role-playing the role the devas play in creating and sustaining and even destroying the universe. Having acknowledged the Gods, and given them offerings to their satisfaction, a petition is made to them — for children, gold, grain, cattle, horses, power, fame, health — before they are allowed to go (visarjan).
But in yagna, the Gods have no form. And they have no permanent residence. They come from the realm of the stars and so the yagna is performed in open air. Yagna could not be performed during rainy seasons, the four monsoon months (chatrumaas) which became linked to inauspiciousness. But, about 2,000 years ago, increasingly Gods were seen as images and icons housed in caves and in temples. These sacred icons (archa) were venerated (archana). The ritual involved the same principles as the Vedic yagna — inviting the God to inhabit the image built, then bathing and decorating and feeding and praising and feeding and entertaining that image, before the petition is made. The devotee gives in order to get. While humans were bound by debt (rinn), and had obligations, the Gods were free of debt and so had no obligations. They were untouched by karma. And so what they gave was dependent on their grace! The devotee (bhakta) hence worshipped (bhaja) the divine being (bhagavan) and sought his grace (prasad). This is an exchange, a giving for receiving, unlike a covenant or a contract, which is about giving and taking and obligations that is cornerstone of Abrahmic religions. Exchange (yagna) connects (yoga) the world by establishing relationships (bandhu). Thus, through yagna and puja, we can theoretically connect with the infinite.







Recent Comments